Linux Distros For Hackers 2026
In the ever-evolving landscape of cybersecurity, staying ahead requires more than just skill; it demands the right tools. As we step into 2026, the digital frontier has become more complex, with emerging threats like advanced persistent threats, ransomware, and AI-driven social engineering attacks reshaping the battlefield.
At BuzzSpot, we recognize the challenges and aspirations of ethical hackers and cybersecurity enthusiasts. Whether you're a seasoned penetration tester or a curious newcomer, the choice of your operating system can significantly impact your effectiveness. Linux distributions tailored for hacking offer a suite of tools and environments designed to empower you in this digital age.
In this comprehensive guide, we'll delve into the best Linux distributions for hackers in 2025, exploring their features, strengths, and ideal use cases. From the renowned Kali Linux to the privacy-focused Tails OS, discover which distro aligns with your cybersecurity journey.
 |
| Linux Distros For Hackers |
Why Linux Is the Hacker’s OS of Choice
In the realm of cybersecurity, the tools you choose can define your success. For ethical hackers and penetration testers, Linux stands out as the operating system of choice. But what makes Linux so appealing to the hacking community?
Open-Source Transparency
Linux's open-source nature means its source code is freely available for anyone to inspect, modify, and enhance. This transparency allows hackers to understand the system's inner workings, identify potential vulnerabilities, and customize the OS to suit their specific needs. Unlike proprietary systems, where the code is hidden, Linux offers a level of visibility that's invaluable for in-depth security analysis.
Powerful Command-Line Interface (CLI)
The command-line interface is a cornerstone of Linux's appeal. It provides a streamlined, efficient way to execute tasks, write scripts, and automate processes. For hackers, the CLI offers granular control over the system, enabling them to perform complex operations with precision and speed.
Comprehensive Suite of Security Tools
Linux distributions often come equipped with a vast array of built-in tools and utilities tailored for security assessments. From network analyzers to penetration testing frameworks, these tools are readily available and frequently updated, providing hackers with a robust toolkit for exploring and securing digital environments.
Robust Security Architecture
Linux is renowned for its stability and security features. Its permission-based model ensures that users operate with the least privileges necessary, reducing the risk of unauthorized access. Additionally, security modules like AppArmor and SELinux provide enhanced access controls, confining processes and minimizing potential attack surfaces.
Customization and Flexibility
One of Linux's standout features is its high degree of customization. Users can tailor the operating system to their exact specifications, from modifying the kernel to adjusting system parameters. This flexibility allows hackers to create an environment optimized for their specific tasks, whether it's penetration testing, digital forensics, or network analysis.
Active and Supportive Community
The Linux community is a vibrant ecosystem of developers, security professionals, and enthusiasts. This collaborative environment fosters knowledge sharing, rapid problem-solving, and continuous improvement of tools and distributions. For hackers, this means access to a wealth of resources, tutorials, and support networks.
In summary, Linux's open-source transparency, powerful CLI, comprehensive security tools, robust architecture, customization capabilities, and active community make it the preferred operating system for hackers. Its features align seamlessly with the needs of cybersecurity professionals, providing a solid foundation for ethical hacking endeavors.
Key Features to Look for in a Hacking-Focused Linux Distribution
Selecting the right Linux distribution for ethical hacking is crucial for effective cybersecurity operations. An ideal distro should offer a blend of robust tools, flexibility, and security features. Here are the essential attributes to consider:
Comprehensive Pre-Installed Toolset
A top-tier hacking distro should come equipped with a wide array of security tools out-of-the-box. For instance, Kali Linux includes over 600 tools covering various aspects of cybersecurity, such as:
- Network Scanning: Nmap
- Packet Analysis: Wireshark
- Password Cracking: John the Ripper
- Wireless Testing: Aircrack-ng
- Exploitation Frameworks: Metasploit
Having these tools readily available saves time and ensures a standardized environment for testing.
Regular Updates and Active Community Support
Cybersecurity is a rapidly evolving field. Distributions that receive frequent updates ensure that users have access to the latest tools and security patches. An active community can also provide support, share knowledge, and contribute to the distro's development.
Hardware Compatibility and Performance
The distribution should be compatible with a wide range of hardware, from high-end machines to older systems. Lightweight desktop environments like Xfce, used in BackBox, can enhance performance on less powerful hardware.
Strong Security and Privacy Features
Security-focused distros should incorporate features like:
- Encrypted Installations: Protects data during and after installation.
- Secure Communication Tools: Includes applications like OpenSSH for encrypted connections.
- Forensics Mode: Prevents writing to disks, preserving the integrity of evidence during analysis.
These features are vital for maintaining operational security and data integrity.
Customization and Flexibility
A good hacking distro should allow users to tailor the environment to their specific needs. This includes the ability to add or remove tools, customize the user interface, and configure system settings. Distributions like Kali Linux offer extensive customization options, enabling users to create personalized toolsets and custom ISOs.
Live Boot and Persistence Capabilities
The ability to run the operating system from a USB or DVD without installation (Live Boot) is essential for fieldwork and testing on different machines. Persistence mode allows users to save changes and data across sessions, which is particularly useful for ongoing projects.
Multi-Platform Support
Support for various platforms, including desktops, laptops, and mobile devices, enhances the versatility of the distribution. For example, Kali NetHunter extends Kali Linux's capabilities to Android devices, facilitating on-the-go penetration testing.
Integration with Security Modules
Advanced security modules like Security-Enhanced Linux (SELinux) provide mandatory access controls, enhancing the overall security posture of the system. These modules offer fine-grained control over system processes and resources.
By prioritizing these features, ethical hackers and cybersecurity professionals can select a Linux distribution that aligns with their operational requirements and enhances their effectiveness in the field.
Top Linux Distributions for Hackers in 2026
In 2026, the landscape of cybersecurity continues to evolve, and selecting the right Linux distribution is crucial for ethical hackers and cybersecurity professionals. Below is a curated list of the top Linux distributions tailored for hacking, each offering unique features to cater to various needs and expertise levels.
Kali Linux: The Gold Standard
Developed by Offensive Security, Kali Linux remains the go-to distribution for penetration testing and ethical hacking.
 |
| Kali Linux |
Key Features:
- Over 600 pre-installed security tools, including Metasploit, Nmap, Wireshark, and John the Ripper.
- Support for multiple desktop environments: GNOME, KDE, and Xfce.
- Customizable ISO images tailored to specific needs.
- Kali NetHunter for mobile penetration testing on Android devices.
Best Use Cases:
- Network penetration testing.
- Wireless attacks.
- Web application exploitation.
- Digital forensics.
Kali Linux offers a balance between user-friendliness and advanced features, making it suitable for both newcomers and seasoned professionals.
Parrot Security OS: Lightweight and Versatile
Parrot Security OS is a Debian-based distribution designed for penetration testing, digital forensics, and privacy protection.
 |
| Parrot OS |
Key Features:
- Pre-installed tools for security testing, programming, and development.
- Integration with Tor and AnonSurf for anonymous browsing.
- Sandboxing and isolation features for executing code safely.
- Lightweight design suitable for older hardware.
Best Use Cases:
- Cloud penetration testing.
- Malware analysis.
- Reverse engineering.
- Secure communications.
Parrot Security OS stands out for its combination of security tools and privacy features, catering to both professionals and enthusiasts.
BlackArch Linux: Power for Advanced Users
Built on Arch Linux, BlackArch is tailored for security researchers and penetration testers seeking a comprehensive toolset.
 |
| BlackArch Linux |
Key Features:
- Repository of over 3,000 security tools.
- Modular architecture allowing installation over existing Arch Linux setups.
- Lightweight and highly configurable, favoring command-line operations.
- Support for ARM devices like Raspberry Pi.
Best Use Cases:
- Advanced penetration testing.
- Reverse engineering research.
- Security assessments on diverse hardware platforms.
BlackArch is ideal for users comfortable with command-line interfaces and seeking an extensive array of specialized tools.
BackBox: User-Friendly and Efficient
BackBox is an Ubuntu-based distribution focusing on providing a robust platform for security assessments and penetration testing.
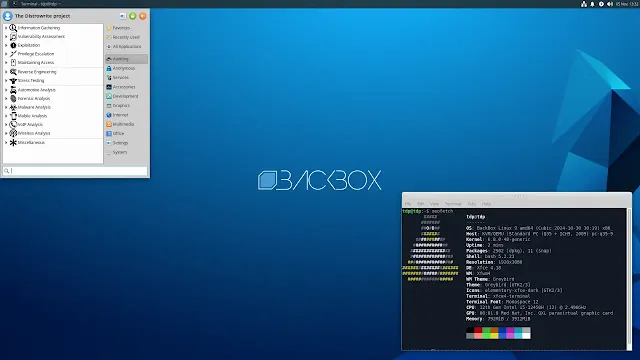 |
| BackBox |
Key Features:
- Pre-installed tools for web application analysis, network assessment, and forensic analysis.
- Lightweight desktop environment ensuring efficient performance.
- Regular updates and active community support.
- Intuitive interface suitable for users transitioning from other operating systems.
Best Use Cases:
- Web application penetration testing.
- Network vulnerability assessments.
- Forensic investigations.
BackBox offers a balance between functionality and ease of use, making it accessible for both beginners and experienced professionals.
Tails OS: Privacy and Anonymity Focused
Tails (The Amnesic Incognito Live System) is a live operating system that prioritizes privacy and anonymity.
 |
| Tails OS |
Key Features:
- Runs from a USB stick or DVD, leaving no trace on the host system.
- All internet traffic routed through the Tor network.
- Includes tools for secure communication and encryption.
- Regularly updated to address security vulnerabilities.
Best Use Cases:
- Secure browsing and communication.
- Whistleblowing and journalism.
- Conducting research without leaving digital footprints.
While not a traditional hacking distribution, Tails is essential for activities requiring high levels of privacy and anonymity.
CAINE: Digital Forensics Specialist
CAINE (Computer Aided INvestigative Environment) is an Italian GNU/Linux live distribution focused on digital forensics.
 |
| CAINE |
Key Features:
- Pre-loaded with tools for forensic analysis and investigation.
- User-friendly GUI environment for ease of navigation.
- Designed to run as a live image to prevent tampering with the host system.
- Facilitates structured reporting of forensic analyses.
Best Use Cases:
- Digital forensic investigations.
- Data recovery and analysis.
- Training and education in forensic methodologies.
CAINE provides a specialized environment for professionals engaged in digital forensic work, emphasizing data integrity and comprehensive analysis.
Security Onion: Comprehensive Threat Detection and Network Monitoring
Security Onion is a free and open-source Linux distribution designed for enterprise security monitoring, intrusion detection, and log management. Built by defenders for defenders, it integrates a suite of powerful tools to provide deep visibility into network and host activities.
 |
| Security Onion |
Key Features:
- Integrated IDS/IPS Tools: Combines Suricata and Zeek for robust network traffic analysis, enabling detection of suspicious activities and potential threats.
- Comprehensive Log Management: Utilizes the ELK Stack (Elasticsearch, Logstash, and Kibana) for efficient log collection, storage, and visualization, facilitating effective incident response and forensic investigations.
- Host-Based Intrusion Detection: Incorporates OSSEC to monitor system logs and file integrity on individual hosts, enhancing overall security posture.
- User-Friendly Interfaces: Features web-based interfaces like Squert and Kibana, providing intuitive dashboards for analyzing security events and network traffic.
- Scalability and Flexibility: Designed to scale from small networks to large enterprise environments, supporting both standalone and distributed deployments.
Best Use Cases:
- Enterprise Security Monitoring.
- Threat Hunting and Incident Response.
- Digital Forensics.
Security Onion stands out as a robust platform for cybersecurity professionals aiming to enhance their organization's security infrastructure through comprehensive monitoring and analysis.
How to Choose the Right Linux Distribution for Hacking
Selecting the ideal Linux distribution for hacking is a pivotal decision that hinges on various factors, including your experience level, specific objectives, hardware capabilities, and the nature of your cybersecurity endeavors. Here's a comprehensive guide to assist you in making an informed choice:
Assess Your Experience Level
- Beginner-Friendly Options: If you're new to ethical hacking, consider distributions like Parrot Security OS or BackBox. These offer user-friendly interfaces and come pre-installed with essential tools, making the learning curve more manageable.
- Intermediate to Advanced Users: For those with a solid foundation in Linux and cybersecurity, Kali Linux provides a comprehensive suite of tools and customization options.
- Expert-Level Distributions: Seasoned professionals seeking extensive toolsets and customization might opt for BlackArch Linux, which offers over 3,000 security tools but requires advanced Linux proficiency.
Define Your Specific Use Case
- Penetration Testing: Distributions like Kali Linux and Parrot Security OS are tailored for penetration testing, offering a wide array of tools for network and application assessments.
- Digital Forensics: If your focus is on forensic analysis, CAINE provides specialized tools for data recovery and investigation.
- Privacy and Anonymity: For activities requiring high levels of anonymity, Tails OS routes all internet traffic through the Tor network and leaves no trace on the host system.
- Enterprise Security Monitoring: Organizations seeking comprehensive monitoring solutions might consider Security Onion, which integrates tools for intrusion detection and log management.
Evaluate Hardware Compatibility
- Resource-Constrained Systems: If you're operating on older or less powerful hardware, lightweight distributions like Parrot Security OS and BackBox are optimized for performance on such systems.
- High-Performance Requirements: Distributions like Security Onion may require more robust hardware due to their comprehensive monitoring and analysis capabilities.
Consider Update and Support Models
- Rolling Releases: Distributions like BlackArch Linux follow a rolling release model, providing the latest updates and tools continuously.
- Stable Releases: If stability is a priority, distributions like BackBox offer regular, stable releases, ensuring consistent performance.
Examine Tool Availability and Customization
- Comprehensive Toolsets: Kali Linux and BlackArch Linux offer extensive repositories of security tools, catering to a wide range of cybersecurity tasks.
- Customization Options: Distributions like Parrot Security OS provide flexibility, allowing users to tailor the system to their specific needs, whether for development, testing, or secure communications.
By carefully evaluating these factors, you can select a Linux distribution that aligns with your hacking objectives and technical proficiency. In the next section, we'll explore real-world scenarios to illustrate how these distributions perform in practical applications.
Future Trends in Linux Distributions for Hackers in 2026
As the cybersecurity landscape evolves, Linux distributions tailored for ethical hacking are integrating cutting-edge technologies to address emerging threats and challenges. Here's an overview of the key trends shaping these distributions in 2026:
- Integration of Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning: Modern Linux distributions are increasingly incorporating AI and ML to enhance threat detection and response capabilities. For instance, adaptive firewalls now leverage machine learning algorithms to analyze network traffic patterns dynamically, identifying and mitigating threats in real-time.
- Adoption of Zero Trust Architecture (ZTA): The shift towards Zero Trust models is evident in the latest Linux distributions. By enforcing strict access controls and continuous verification, ZTA ensures that no user or device is inherently trusted, enhancing overall security posture.
- Emphasis on Quantum-Resistant Cryptography: With advancements in quantum computing, there's a growing focus on integrating quantum-resistant encryption algorithms into Linux distributions. This proactive approach aims to safeguard data against potential future quantum threats.
- Modular and Customizable Architectures: Flexibility is becoming a hallmark of modern Linux distributions. Users can now tailor their environments by selecting specific modules or tools, ensuring that the system aligns precisely with their operational needs.
- Enhanced Cloud and Container Support: Recognizing the shift towards cloud-native applications, Linux distributions are optimizing for seamless integration with cloud platforms and containerization technologies like Docker and Kubernetes. This ensures scalability and efficient deployment in diverse environments.
- Continuous Rolling Releases and Automated Updates: To keep pace with the rapidly evolving threat landscape, many distributions are adopting rolling release models. This approach ensures users have access to the latest tools and security patches without waiting for major version updates.
- Integration of Behavioral Biometrics: Some distributions are exploring the incorporation of behavioral biometrics, analyzing user behaviors such as typing patterns and mouse movements to enhance authentication mechanisms. This adds an additional layer of security by detecting anomalies that may indicate unauthorized access.
These trends underscore the dynamic nature of Linux distributions in the realm of ethical hacking. By embracing these innovations, users can ensure they are equipped with robust tools and features to navigate the complex cybersecurity landscape of 2026 and beyond.
Final Recommendations
After exploring the top Linux distributions tailored for ethical hacking and cybersecurity in 2025, it's essential to align your choice with your specific needs, experience level, and operational requirements. Here's a concise guide to help you make an informed decision:
For Beginners and Learners:
- Parrot Security OS: Ideal for newcomers, Parrot OS offers a user-friendly interface with a rich collection of security tools. Its lightweight nature ensures smooth performance on various hardware configurations.
- BackBox: Based on Ubuntu, BackBox provides a familiar environment for those new to Linux. It includes essential tools for web application analysis and network assessment, making it a solid starting point for aspiring ethical hackers.
For Intermediate Users:
- Kali Linux: A staple in the cybersecurity community, Kali Linux comes pre-installed with over 600 penetration-testing tools. Its active community and extensive documentation make it suitable for users looking to deepen their skills.
- Parrot Security OS (Security Edition): Beyond its beginner-friendly Home Edition, Parrot's Security Edition caters to users seeking advanced tools for penetration testing, vulnerability assessment, and digital forensics.
For Advanced Professionals:
- BlackArch Linux: Tailored for seasoned security researchers, BlackArch boasts a repository of over 2,500 tools. Its Arch Linux base ensures a rolling release model, providing the latest updates and features.
- Security Onion: Designed for enterprise security monitoring, Security Onion integrates tools for intrusion detection, log management, and network security monitoring. It's best suited for professionals managing large-scale security operations.
For Privacy and Anonymity:
- Tails OS: Tails prioritizes user anonymity by routing all internet traffic through the Tor network and leaving no trace on the host system. It's an excellent choice for journalists, activists, and individuals operating in high-risk environments.
For Digital Forensics:
- CAINE (Computer Aided INvestigative Environment): CAINE offers a comprehensive suite of forensic tools, making it invaluable for professionals involved in digital investigations and data recovery.
Selecting the right Linux distribution hinges on your specific objectives, technical proficiency, and the nature of your cybersecurity tasks. Whether you're embarking on your ethical hacking journey or managing complex security infrastructures, there's a distribution tailored to your needs. Stay updated with the latest developments, engage with community forums, and continuously hone your skills to navigate the ever-evolving cybersecurity landscape effectively.
